Blog
What is circular packaging?
The packaging industry is undergoing a transformation as sustainability and circularity become top global priorities. As consumers demand more sustainable options and regulations tighten, circular packaging has become essential to sustainable business practices. But what does circular packaging actually mean and why is it essential for the future of packaging?
Defining circular packaging
Circular packaging moves away from the traditional ‘make, use, dispose’ model by focusing on designing materials for continuous use. This helps to eliminate waste and make the best use of resources. A key aspect is using sustainable materials, such as renewable or recycled inputs, to reduce environmental impact. This approach aligns with global sustainability trends, such as using more recycled content to cut down on virgin resources. Another important factor is creating packaging that lasts longer and can be reused, using innovative designs to extend material life cycles and rethinking standard packaging methods.
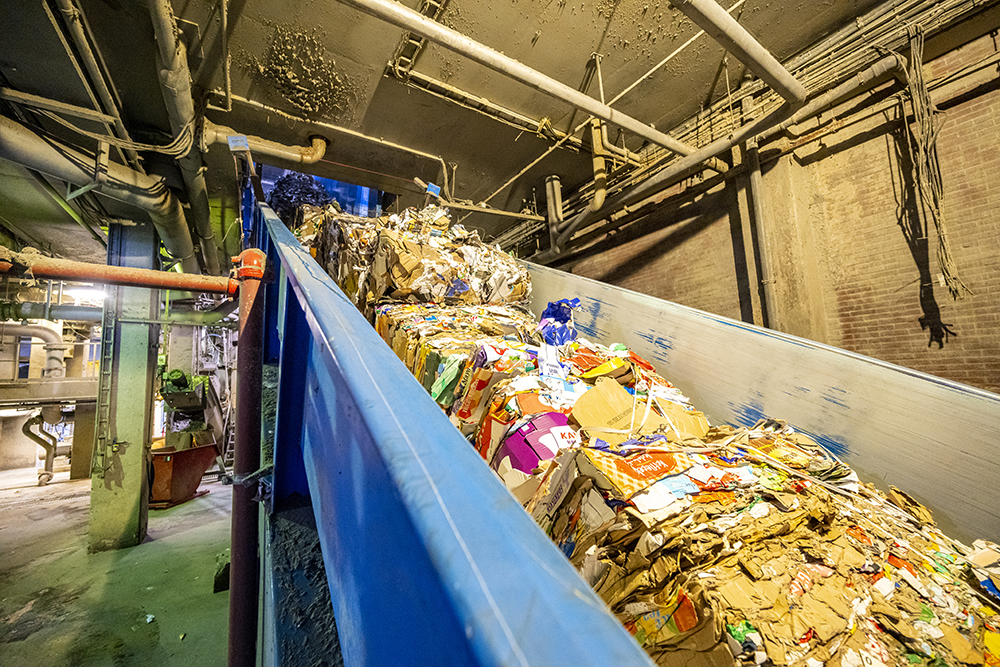
To close the loop, circular packaging relies on efficient recyclability to ensure materials can be returned to production, supporting a truly circular economy. By reducing emissions and conserving resources, it strives for a minimal environmental footprint, in line with international initiatives such as the European Green Deal to promote resource efficiency and reduce waste across all industries.
The circular economy connection
Circular packaging is a cornerstone of the circular economy, a model that aims to replace the traditional take-make-waste approach. This regenerative framework aims to decouple economic growth from resource consumption, promoting sustainable cycles of production and consumption.
Through circular packaging, industries can:
- Reduce dependence on finite natural resources by prioritising recycled materials.
- Reduce greenhouse gas emissions, as recycled materials can require less energy to produce than virgin materials.
- Minimise waste by designing products that can be reused or recycled, rather than discarded for incineration or even landfill.
The European Union’s Circular Economy Action Plan (CEAP) is one of the driving forces behind this shift, encouraging businesses to adopt circular principles throughout their operations.
Benefits of circular packaging
For consumers
- Environmental impact: Circular packaging meets the growing demand for sustainable products, enabling consumers to make more sustainable choices.
- Improved safety and quality: Innovations in materials and design improve food safety, extend shelf life and reduce spoilage, directly benefiting the end consumer.
- Transparency: Labelling and information associated with circular packaging builds trust by communicating sustainability efforts
For businesses
- Cost efficiency: Circular packaging reduces long-term costs by optimising material use, recycling and transportation.
- Regulatory compliance: Compliance with EU regulations (see below) helps businesses avoid penalties and remain competitive.
- Market differentiation: Companies that adopt circular packaging can position themselves as sustainability leaders, enhancing brand reputation.
- Reduced carbon footprint: Circular packaging designs can significantly reduce the impact of a brand’s overall carbon footprint.
Tackling Scope 3 emissions in packaging
Scope 3 emissions are indirect greenhouse gas emissions from a company’s value chain, such as those caused by suppliers, customers or the use and disposal of the company’s products. They are among the most difficult to address, but represent a significant opportunity for positive impact. For packaging, these emissions come from activities such as raw material production, transportation and disposal. It is estimated that packaging contributes up to 20% of a brand’s total carbon footprint.
How to reduce Scope 3 emissions
- Material selection: Choose recycled materials that require less energy-intensive production processes.
- Efficient design: Space-efficient packaging reduces transport emissions.
- Supplier collaboration: Engaging suppliers to adopt sustainable practices and provide transparency on emissions data supports better decision making.
- Life cycle assessments: Understanding the total environmental impact of packaging through life cycle analysis can identify opportunities to reduce emissions.
By addressing Scope 3 emissions, companies can meet regulatory requirements and consumer expectations while demonstrating sustainability leadership.
Learn more about Solidus’s efforts to address Scope 3 emissions.
The role of legislation
The European Union has set ambitious targets to accelerate the shift towards sustainability. Circular packaging is central to achieving these goals. Key legislative frameworks include:
- Packaging and Packaging Waste Regulation (PPWR): Aims to ensure that all packaging in the EU is reusable or recyclable by 2030, with targets to reduce waste and increase recycling rates.
- Circular Economy Action Plan (CEAP): Introduced as part of the European Green Deal, this plan focuses on creating a sustainable product policy framework that encourages the reuse of resources.
- Single-Use Plastics Directive (SUPD): Aims to reduce plastic waste, particularly in the marine environment, and promote the use of alternative materials.
Understanding these frameworks is crucial for businesses looking to future-proof their operations. Brands that comply with these regulations will avoid legal challenges and benefit from improved efficiency and consumer trust.
Circular packaging is more than a trend – it is a necessity. It addresses global challenges such as resource scarcity, climate change and waste management, while delivering tangible benefits to businesses and consumers. By embracing circular principles, companies can reduce their environmental footprint, comply with evolving regulations and meet the growing demand for sustainable practices.
Solidus can help you stay ahead in the evolving packaging landscape with circular packaging solutions tailored to meet your needs. Contact us now to explore how we can drive your packaging innovation forward.